Online Field Guide to The Reptiles and Amphibians of Arizona
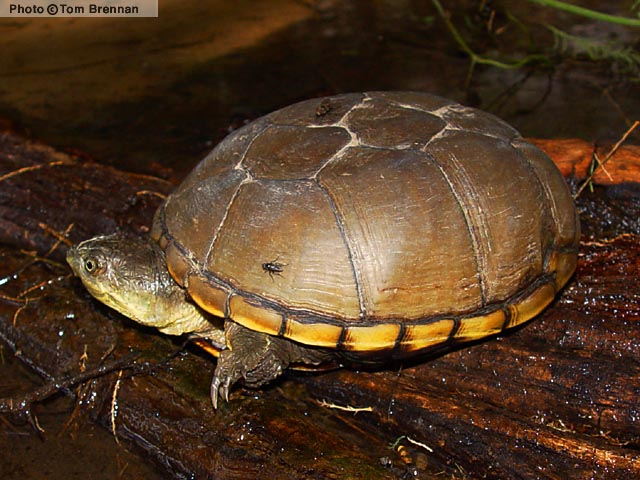



Graham County, AZ
| YELLOW MUD TURTLE Kinosternon flavescens | |
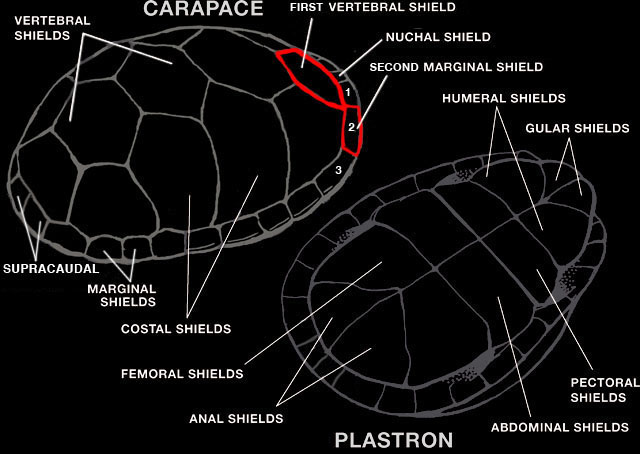
| DESCRIPTION: A small (shell up to 165 mm or 6.5″ in length ) turtle with a dome shaped shell. The carapace is flat on top and is usually olive-brown to yellow-brown in color. The marginal shields (see figure below) are often yellow. The underside of the shell (plastron) is yellow and has two hinges so that the front and back can close when the turtle retreats inside. The top of the head is gray or brown and there are small, fleshy projections on the throat. The throat and sides of the face are plain yellow or cream distinguishing this turtle from the similar looking Sonora Mud Turtle which has reticulations on the head and neck. The first vertebral shield of the Yellow Mud Turtle is in contact with the second marginal shield (see figure below) distinguishing it from the similar looking Arizona Mud Turtle.
DISTRIBUTION: It is found in a small portion of southeastern Arizona at elevations ranging from about 3,000′ to 4,000′. HABITAT: In Arizona it is an inhabitant of Chihuahuan Desertscrub and Semidesert Grassland communities. Found primarily in low valley bottoms, usually in or near sources of permanent or temporary water. It frequents pools within washes, ponds, cattle tanks, large puddles, and ditches. BEHAVIOR: A semi-aquatic turtle that is most active during the day. During the warm season it spends most of its time in the water. Occasionally travels overland during rainy conditions. Hibernates in an underground burrow during the cold months of winter and aestivates underground during the hot, dry summer months. When captured or threatened it may emit a foul smelling musk from glands on the sides of the body. REPRODUCTION: Mating takes place in summer and a clutch of up to 10 brittle-shelled eggs are laid in an underground nest in summer. Females may remain in the nest with the eggs for several days after laying them. By Thomas C. Brennan
|
|
| Brennan, T. C., & A. T. Holycross. 2006. A Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles in Arizona. Arizona Game and Fish Department. Phoenix, AZ
Stebbins, R.C. 1951. Amphibians of Western North America. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA. Stebbins. 1985. Western Reptiles and Amphibians. Houghton Mifflin. New York, NY Stebbins, R.C. 2003. A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians, Third Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, MA. |
|
Visit Partners in Amphibian and Reptile Conservation:


HOME
Copyright © 2023, Arizona Game and Fish Department. All rights reserved.
If you make use of the textual contents of this site in reports, publications, etc. please cite and credit the author(s) and photographer(s). All photos on this website are copyrighted. However, those found in the species account section may be used for any noncommercial scientific, educational, or conservation purposes provided that photographs are not altered and continue to bear the copyright symbol and name of the photographer. Please contact the photographer regarding commercial use of copyrighted photographs.










