Online Field Guide to The Reptiles and Amphibians of Arizona



Santa Cruz County, AZ
 Arizona |
| BLACK-NECKED GARTERSNAKE Thamnophis cyrtopsis |
Non-Venomous
|
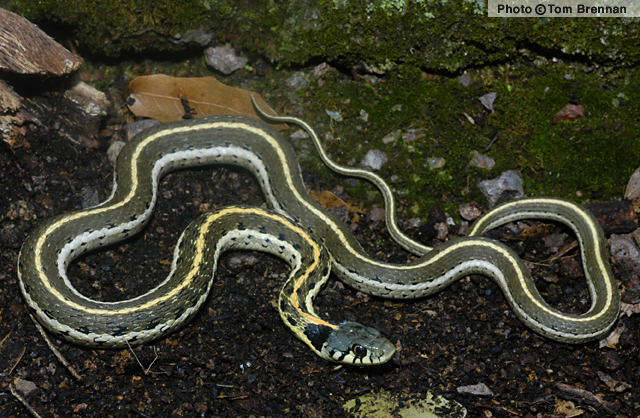
| DESCRIPTION: A medium (up to 1,070 mm or 42″ in total length) dark olive-gray snake with a single orange-yellow stripe down the middle of the back (mid-dorsal stripe) and an additional cream or white stripe along each lower side on the 2nd and 3rd scale rows (counting up from the belly). The mid-dorsal stripe is usually orange on the neck grading to pale yellow on the posterior portion of the body. Two large, jet black, crescent-shaped blotches mark the neck. The top of the head is plain gray or blue-gray. Small, black blotches mark the dark areas between the stripes on the anterior portion of the body. The underside is plain pale gray or cream. Dark bars mark the seams of the upper lip scales (upper labials). The pupils are round and the dorsal scales are keeled.
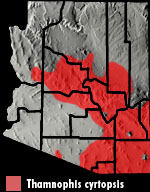
DISTRIBUTION: This snake is found across southeastern and central Arizona. An isolated population exists in the Ajo Mountains of western Pima County. In Arizona it ranges in elevation from 1,100′ in the Phoenix basin to about 7,000′ in Mogollon Rim country. HABITAT: It inhabits a wide variety of biotic communities including Sonoran Desertscrub, Semidesert Grassland, Interior Chaparral, Madrean Evergreen Woodland, Great Basin Conifer Woodland, Plains Grassland, Great Basin Grassland, and Petran Montane Conifer Forest. It is usually found near water in rocky upland canyons and along semi-permanent streams and drainages. It occasionally wanders far from water. BEHAVIOR: Although primarily diurnal and crepuscular it is occasionally active on warm nights. It is often encountered mid-morning or late afternoon foraging for tadpoles in shallow water. It hibernates during the cold months of late fall and winter. DIET: In addition to tadpoles this snake eats frogs, toads, lizards, salamanders, earthworms, and invertebrates. REPRODUCTION: It gives birth to up to up to 25 young in late spring or summer. By Thomas C. Brennan Bartlett. 2000. Snakes of North America: Western Region. Gulf Publishing Co. Houston, TX Brennan, T. C., and A. T. Holycross. 2006. A Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles in Arizona. Arizona Game and Fish Department. Phoenix, AZ Brennan, T. C., and A. T. Holycross. 2005. A Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles of Maricopa County. Arizona Game and Fish Department. Phoenix, AZ Degenhardt, W. G., Painter, C. W., and Price, A. H.. 1996. Amphibians and Reptiles of New Mexico. University of New Mexico Press. Albuquerque. Fowlie. 1965. The Snakes of Arizona. Azul Quinta Press, Fallbrook, CaliforniaStebbins. 1985. Western Reptiles and Amphibians. Houghton Mifflin. New York, |
|
Visit Partners in Amphibian and Reptile Conservation:


HOME
Copyright © 2023, Arizona Game and Fish Department. All rights reserved.
If you make use of the textual contents of this site in reports, publications, etc. please cite and credit the author(s) and photographer(s). All photos on this website are copyrighted. However, those found in the species account section may be used for any noncommercial scientific, educational, or conservation purposes provided that photographs are not altered and continue to bear the copyright symbol and name of the photographer. Please contact the photographer regarding commercial use of copyrighted photographs.