Online Field Guide to The Reptiles and Amphibians of Arizona



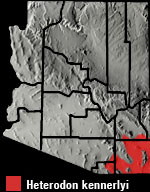
Cochise County, AZ
 Cochise Co., AZ |
| MEXICAN HOG-NOSED SNAKE Heterodon kennerlyi |
Mildly Venomous
|
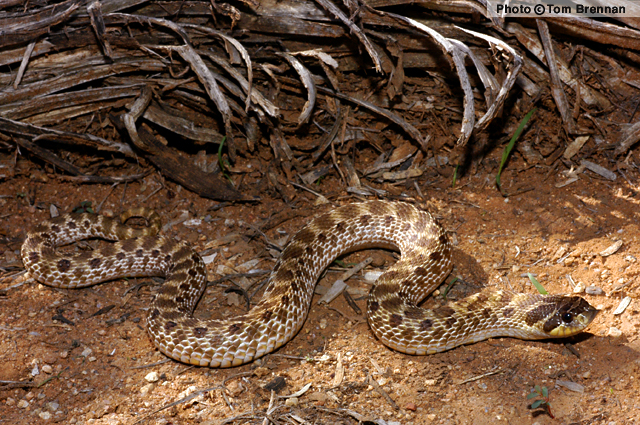
| DESCRIPTION: A medium (up to 760 mm or 30″ in total length), stocky, yellowish-tan snake with 23-43 brown to orange-brown dorsal blotches. The large mid-dorsal blotches are often somewhat muted. A row of small, dark brown, crisp-edged blotches runs along each upper side. Below this row, an additional row of large, muted, blotches runs along each side, followed below by one or two more rows of small muted blotches or spots. The dorsal blotches morph into bands on the tail. Two large, crisp-edged, dark brown blotches mark the neck and are separated at the mid-dorsum by a third, smaller nuchal blotch. Two dark brown bars cross the top of the head between the eyes, the posterior-most of which runs past the back of the eye and down to the corner of the mouth. The underside of the body is checkered with large, rectangular, yellow-orange and black blotches. Many specimens have a nearly solid black venter. The underside of the tail is usually black. The pupils are round. The head is large but is barely distinct from the thick neck. The scale on the snout (rostral) is enlarged, flat on bottom, upturned, keeled on top, and shovel-like. Adult females attain larger sizes than males. The dorsal scales are keeled. The similar looking Chihuahuan Hook-nosed Snake has smooth (not keeled) dorsal scales and a pale venter.
DISTRIBUTION: This snake is found in the valleys of southeastern Arizona at elevations ranging from ca. 1,100 m to 1,560 m (3,600′ – 5,100′). HABITAT: Heterodon kennerlyi is usually found within Semidesert Grassland, Chihuahuan Desertscrub, and grassland communities. It seems to prefer open areas with loose, well-drained, sandy or gravelly soil. It is typically found in open valleys, flatlands, rolling plains, and gentle bajadas. DIET: Prey is located by smell and sight. The shovel-like snout is used to root around in the soil for prey which includes toads, frogs, lizards, small snakes, rodents, reptile eggs, salamanders, hatchling turtles, birds and their eggs, and insects. There are two enlarged teeth on the posterior of each upper jaw bone (maxilla) which are used to inject a mild venom into prey. The venom might be mildly toxic to humans. Prey is grasped by the jaws and is not constricted but may be partially restrained by a body coil. Heterodon kennerlyi is resistant to the toxic secretions of toads, a major prey item. REPRODUCTION: Most mating takes place in the spring and some might occur in late summer or fall. A clutch of up to 23 eggs is laid, usually in June or July, in a nest excavated from sandy or loamy soil. Incubation lasts 50 to 64 days and hatchlings appear in late July, August, and September. REMARKS: The proliferation of roads through its habitat might negatively impact some populations of H. kennerlyi. This snake frequently basks on warm roads making it particularly susceptible to road mortality. Bartlett. 2000. Snakes of North America: Western Brennan, T. C., and A. T. Holycross. 2006. A Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles in Arizona. Arizona Game and Fish Department. Phoenix, AZ Degenhardt, W. G., Painter, C. W., and Price, A. H.. 1996. Amphibians and Reptiles of New Mexico. University of New Mexico Press. Albuquerque. Fowlie. 1965. The Snakes of Arizona. Azul Quinta Press, Fallbrook, California Lowe, Schwalbe, Johnson. 1986. The Venomous Reptiles of Arizona. Nongame Branch Stebbins. 1985. Western Reptiles and Amphibians. Houghton Mifflin. New York, NY |
|
Visit Partners in Amphibian and Reptile Conservation:


HOME
Copyright © 2023, Arizona Game and Fish Department. All rights reserved.
If you make use of the textual contents of this site in reports, publications, etc. please cite and credit the author(s) and photographer(s). All photos on this website are copyrighted. However, those found in the species account section may be used for any noncommercial scientific, educational, or conservation purposes provided that photographs are not altered and continue to bear the copyright symbol and name of the photographer. Please contact the photographer regarding commercial use of copyrighted photographs.