Online Field Guide to The Reptiles and Amphibians of Arizona



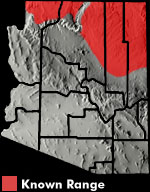
Apache County, AZ
 Apache Co., AZ |
| COMMON SAGEBRUSH LIZARD Sceloporus graciosus | |
|
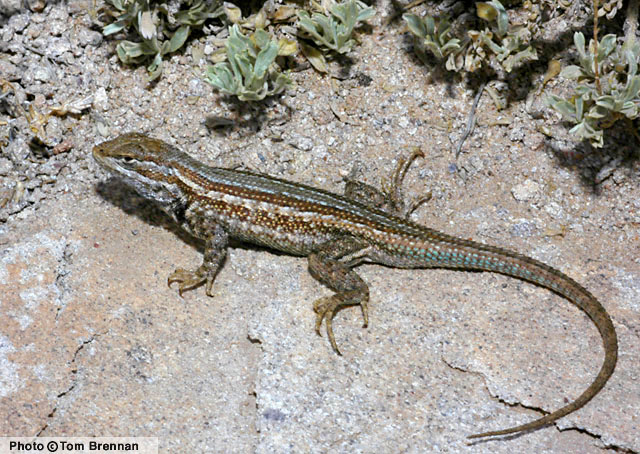
DESCRIPTION: A small (up to 76 mm or 3″ from snout to vent), gray-brown to orange-brown lizard with pointed, keeled scales and four rows of dark, irregular shaped blotches on the back. The blotches in each row often merge together forming a dark, wavy stripe. A broad, gray mid-dorsal stripe extends from the neck onto the base of the tail. A rust or orange patch is often present in each “armpit” area and a dark bar marks each shoulder. The throat is either plain or marked with a uniform blue-gray mottling, often accompanied by pink flecking. Males have two large, blue patches on the belly. Belly patches are often edged with black. On females the belly patches are faint or lacking. During breeding season females may develop a yellow tint on the belly and orange-red suffusions on the neck and sides. Its uniform throat pattern distinguishes this lizard from the similar looking Plateau Lizard and Southwestern Fence Lizard. Its lack of side-blotches distinguishes it from the Common Side-blotched Lizard and Common Lesser Earless Lizard. DISTRIBUTION: It ranges across most of the northern Arizona plateau region including the Arizona Strip (land north of the Colorado River). In Arizona it is found at elevations ranging from about 4,000′ to over 8,500′. HABITAT: A wide variety of biotic communities including Great Basin Desertscrub, Great Basin Conifer Woodland, Petran Montane Conifer Forest, and Petran Subalpine Conifer Forest are home to this lizard. It can be encountered on open, flat, grassy plains and plateaus, wooded foothills, rocky canyons, and on steep forested slopes. It is usually encountered in relatively open, sunlit areas with plenty of basking sites. BEHAVIOR: This diurnal lizard is most active from mid morning through early afternoon. It hibernates during the cold months of fall and winter. It is usually encountered on the ground in the vicinity of cover but it occasionally climbs onto rocks, tree trunks, fence posts, and wood piles to bask. DIET: The Common Sagebrush Lizard feeds on a variety of insects including ants, beetles, termites, true bugs, and grasshoppers. It also eats a variety of spiders and scorpions. REPRODUCTION: Mating takes place in May and June. One to 2 clutches of eggs are laid in June and July. Clutch size ranges from 2 to 10 eggs. Incubation lasts from 44 to 52 days and hatchlings begin to emerge as early as July. By Thomas C. Brennan Brennan, T. C., & A. T. Holycross. 2006. A Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles in Arizona. Arizona Game and Fish Department. Phoenix, AZ Degenhardt, W. G., Painter, C. W., and Price, A. H.. 1996. Amphibians and Reptiles of New Mexico. University of New Mexico Press. Albuquerque. Stebbins, R.C. 2003. A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians, Third Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, MA. |
|
Visit Partners in Amphibian and Reptile Conservation:


HOME
Copyright © 2023, Arizona Game and Fish Department. All rights reserved.
If you make use of the textual contents of this site in reports, publications, etc. please cite and credit the author(s) and photographer(s). All photos on this website are copyrighted. However, those found in the species account section may be used for any noncommercial scientific, educational, or conservation purposes provided that photographs are not altered and continue to bear the copyright symbol and name of the photographer. Please contact the photographer regarding commercial use of copyrighted photographs.