Online Field Guide to The Reptiles and Amphibians of Arizona
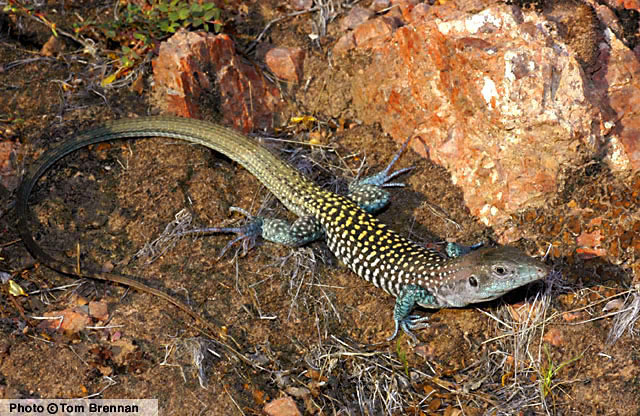



Adult. Maricopa County, AZ
 Juvenile. Maricopa Co., AZ |
| RED-BACKED WHIPTAIL Aspidoscelis xanthonota | |
|
DESCRIPTION: A large (up to 114 mm or 4.5″ from snout to vent), slim, burgundy-brown lizard with a long, thin tail, a slim, pointed snout, and a light orange tint on the lower back. The orange tint on the lower back is restricted to the upper surface and does not extend down onto the sides. The body and hind limbs are marked with light spots. The limbs are tinted with light blue. The tail is tan with small yellow spots near the base. Young animals are dark brown with six (possibly seven) distinct, light colored stripes on the neck and body. As the animal ages it acquires orange and blue tinting, the stripes break up into spots, and additional light spots begin to emerge from the dark spaces between the stripes. Adults are spotted and lack stripes entirely. On the sides of the body the spots often merge together into vertical bars. The scales on the body are small and granular. The scales on the tail are large, keeled, and rectangular. The scales on the belly are large, smooth, and rectangular. The scales on top of the head are large, smooth, and plate-like. The similar looking Tiger Whiptail is smaller and has dark gray or black mottling or reticulations on the sides and chest. HABITAT: Primarily an inhabitant of the Arizona Upland Sonoran Desertscrub community. Usually encountered in mountainous terrain along canyon bottoms and on rocky slopes. It also follows drainages out onto bajadas. It is often encountered near springs, tinajas, and other sources of water. BEHAVIOR: This alert, fast-moving, ground-dweller actively forages during the day. It hibernates during the cold months of winter and late fall. When pursued this wary lizard is very conscious of its proximity to the pursuer and often stays just out of reach. DIET: Prey consists of a variety of insects including ants, termites, beetles, and caterpillars. A variety of spiders are also eaten. REPRODUCTION: Mating takes place in spring and one or two clutches of eggs are laid in summer. Clutch size ranges from 1 to 10 eggs. By Thomas C. Brennan Brennan, T. C., & A. T. Holycross. 2006. A Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles in Arizona. Arizona Game and Fish Department. Phoenix, AZ Brennan, T. C., & A. T. Holycross. 2005. A Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles of Maricopa County. Arizona Game and Fish Department. Phoenix, AZ |
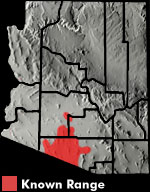 |
Visit Partners in Amphibian and Reptile Conservation:


HOME
Copyright © 2023, Arizona Game and Fish Department. All rights reserved.
If you make use of the textual contents of this site in reports, publications, etc. please cite and credit the author(s) and photographer(s). All photos on this website are copyrighted. However, those found in the species account section may be used for any noncommercial scientific, educational, or conservation purposes provided that photographs are not altered and continue to bear the copyright symbol and name of the photographer. Please contact the photographer regarding commercial use of copyrighted photographs.










