Online Field Guide to The Reptiles and Amphibians of Arizona



Cochise County, AZ
 Cochise Co., AZ |
| GREEN TOAD Anaxyrus debilis | |
|
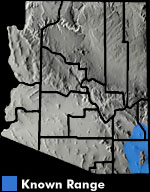
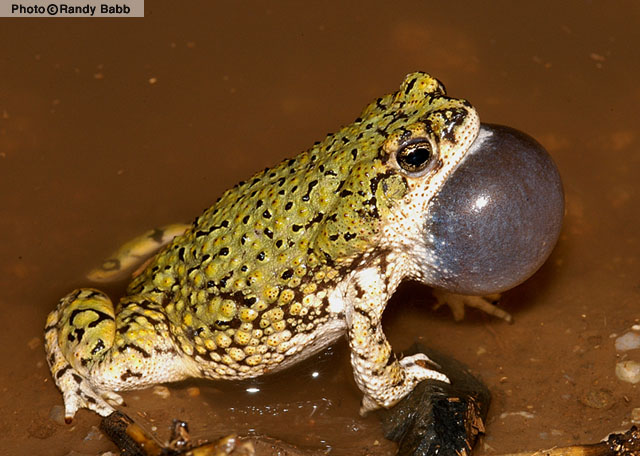
DESCRIPTION: The Green toad is small (to 2 inches in length), flattish toad with a dorsal color of green or yellow-green with small black spots and bars that do not connect to form reticulations (see the description for the similar Sonoran green toad). The ventral surface is white or cream. This species has large, elongated parotoid glands; numerous warts on the back, head, and limbs; and horizontal pupils. The cranial crests are weak or absent. Males have a dark or dusky throat, whereas females have a yellow or white throat. The tadpoles grow to about one inch prior to metamorphosis. Small tadpoles (<0.3 inch) are black, but obtain a mottled pattern as they develop. The ventral surface is light colored and the tail fin is highly arched. DISTRIBUTION: This species ranges from southeastern Colorado and southwestern Kansas south through New Mexico, southeastern Arizona, Texas, and northern Mexico. In Arizona, it is only known from the Sulphur Springs, San Simon, and San Bernardino valleys in the southeastern portion of the state. HABITAT: In Arizona, this secretive, burrowing species inhabits valleys and bajadas characterized by semi-desert grasslands and Chihuahuan Desertscrub. It may occur marginally in Sonoran Desertscrub in the northern end of the San Simon Valley. Within these communities, Green toads are typically found at rain pools, cattle tanks, and other sites that fill with water during the summer monsoon. BEHAVIOR: Primarily nocturnal, this species typically passes the day under surface cover, in rodent burrows, or other subterranean retreats. Some males may be heard calling by day at the peak of the summer breeding season. In Arizona, Green toads are active primarily from July into September. REPRODUCTION AND CALLS: Breeding commences with the first significant, summer monsoon storm and typically lasts only 1-3 days. Breeding in Arizona occurs in ephemeral waters filled by summer rains. Males call from the shoreline or in very shallow water; their call is a nasal, insect-like high-pitched buzz that lasts 2-10 seconds. The call is similar to the Sonoran green toad and Great Plains narrow-mouthed toad. Eggs of this species have not been well described, but one clutch consisted of 1,287 eggs laid singly. Another author reported eggs laid in small strings and attached to vegetation. Eggs probably hatch in 1-2 days and, based on limited information, metamorphosis likely occurs in 2-4 weeks. In southwestern New Mexico, metamorphosing Green toads have been found as late as 27 September, but most metamorphose in late July. DIET: Green toads feed on a variety of small invertebrates, such as ants, small butterflies and moths, beetles, and small grasshoppers. REMARKS: The subspecies Anaxyrus debilis insidior occurs in Arizona. This species is closely related to the Sonoran Green Toad and the Little Mexican toad (Anaxyrus kelloggi) of the Pacific coastal plain and foothills of western Mexico. By Ernest Nigro and Jim Rorabaugh
Degenhardt, W.G., C.W. Painter, and A.H. Price. 1996. Amphibians and Reptiles of New Mexico. University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque. Painter, C.W. 2005. Bufo debilis Girard, 1854, Green Toad. Pages 404-406 in M.J. Lannoo (ed), Amphibian Declines: The Conservation Status of United States Species. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA. Stebbins, R.C. 2003. A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians, Third Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, MA. Sullivan, B.K., K.B. Malmos, E.W.A. Gergus, and R.W. Bowker. 2000. Evolutionary implications of advertisement call variation in Bufo debilis, B. punctatus, and B. retiformis. Journal of Herpetology. 34 (3):368-374. Zweifel, R.G. 1960. Descriptive notes on the larvae of toads of the debilis group, genus Bufo. American Museum Novitates 2407:1-13. |
|
Visit Partners in Amphibian and Reptile Conservation:


HOME
Copyright © 2023, Arizona Game and Fish Department. All rights reserved.
If you make use of the textual contents of this site in reports, publications, etc. please cite and credit the author(s) and photographer(s). All photos on this website are copyrighted. However, those found in the species account section may be used for any noncommercial scientific, educational, or conservation purposes provided that photographs are not altered and continue to bear the copyright symbol and name of the photographer. Please contact the photographer regarding commercial use of copyrighted photographs.